Baby Foreskin Care: A Comprehensive Guide for Parents
Introduction
The foreskin is a delicate and sensitive part of a baby boy’s anatomy. Proper care is essential to prevent infections, discomfort, and future complications. This comprehensive guide will provide parents with detailed information on baby foreskin care, including cleaning, hygiene, and potential medical conditions.
Anatomy of the Foreskin
The foreskin is a retractable skin covering the head (glans) of the penis. It is composed of two layers: the inner layer, which is thin and moist, and the outer layer, which is thicker and protective.
Cleaning the Foreskin
- Newborns: For the first few weeks of life, gently wipe the foreskin with a soft, damp cloth during diaper changes. Do not retract the foreskin.
- Infants: Once the circumcision wound has healed (if applicable), you can gently retract the foreskin and clean the area with warm water and mild soap. Avoid using harsh chemicals or detergents.
- Toddlers: Continue cleaning the foreskin as described above. Encourage your child to retract the foreskin on his own as he becomes more comfortable.
Hygiene
- Diaper Changes: Change diapers frequently to prevent moisture buildup, which can lead to infections.
- Bathing: Bathe your child regularly and gently clean the foreskin with warm water.
- Clothing: Choose loose-fitting, breathable clothing to prevent irritation.
- Avoid Circumcision Trauma: If your child has been circumcised, follow the doctor’s instructions for care and avoid touching the area excessively.
Potential Medical Conditions
- Phimosis: A condition where the foreskin is too tight to retract. This can cause pain, difficulty urinating, and infections.
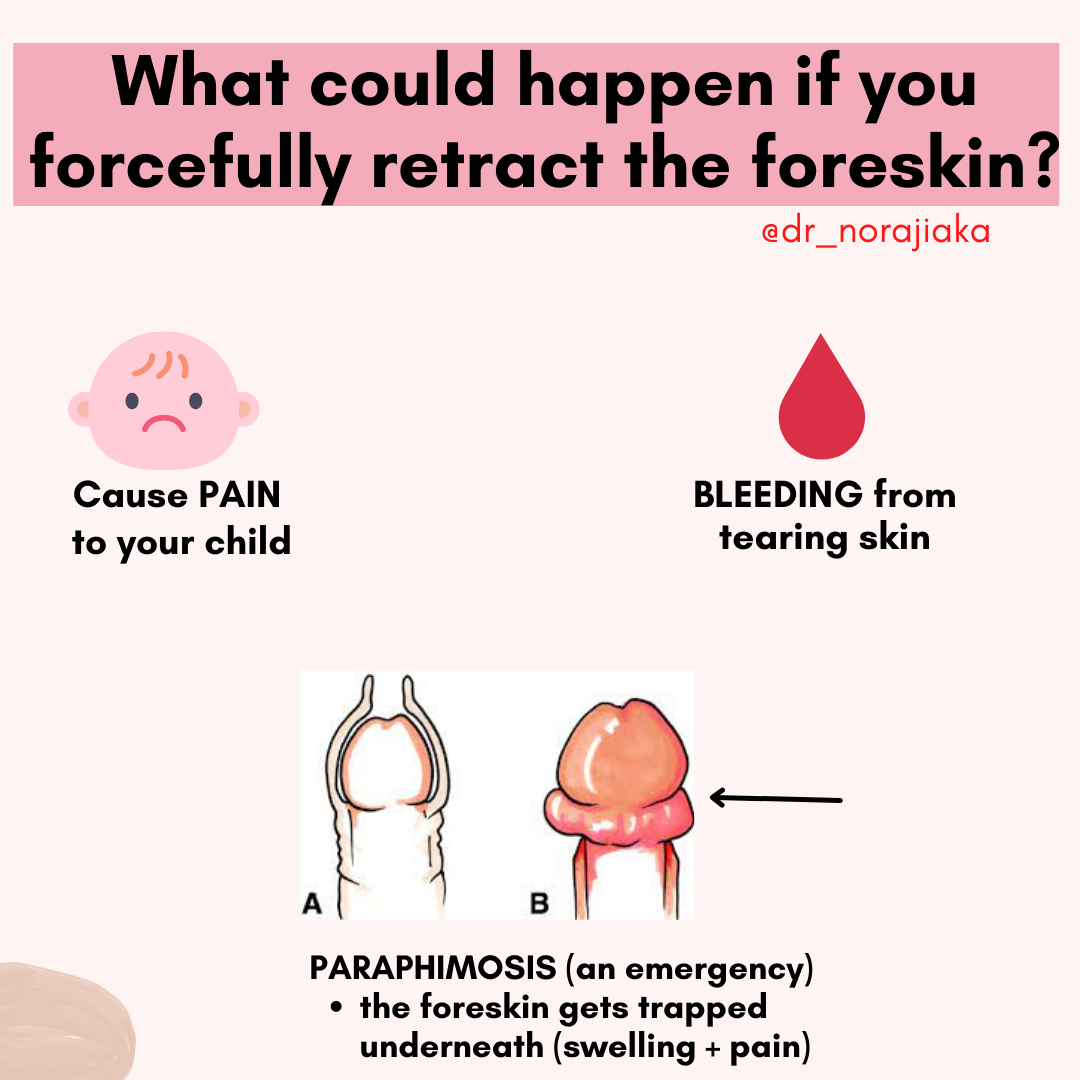
- Paraphimosis: A condition where the foreskin is retracted and cannot be returned to its normal position. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
- Balanitis: An inflammation of the head of the penis. This can be caused by poor hygiene, infections, or allergies.
- Posthitis: An inflammation of the foreskin. This can be caused by similar factors as balanitis.
Signs and Symptoms of Foreskin Problems
- Redness, swelling, or irritation
- Pain or discomfort
- Difficulty urinating
- Discharge or odor
- Skin changes (e.g., thickening, peeling)
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention if your child experiences any of the following:
- Persistent foreskin problems
- Difficulty retracting the foreskin
- Signs of infection (e.g., redness, swelling, discharge)
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Any unusual changes in the foreskin’s appearance or behavior
Circumcision
Circumcision is a surgical procedure to remove the foreskin. It is a personal decision that should be made after careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks.
Benefits of Circumcision:
- Reduced risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in infancy
- Potential protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Easier hygiene
Risks of Circumcision:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Pain
- Cosmetic concerns
Alternatives to Circumcision
- Retraction Method: Gradually retracting the foreskin over time to loosen it.
- Steroid Cream: Applying a topical steroid cream to soften the foreskin.
- Surgery: In severe cases of phimosis or paraphimosis, surgery may be necessary.
Conclusion
Baby foreskin care is an important aspect of a child’s health and well-being. By following the guidelines outlined in this guide, parents can help prevent infections, discomfort, and future complications. If you have any concerns about your child’s foreskin, do not hesitate to seek medical advice.
