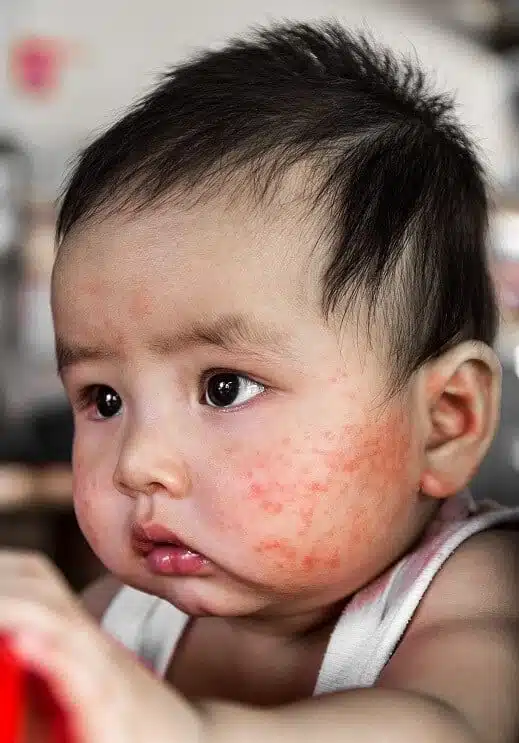
Baby Eczema: A Comprehensive Guide for Parents
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that affects infants and children. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin that can cause significant discomfort. While there is no cure for eczema, there are effective treatments that can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected children.
Causes of Baby Eczema
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the risk factors for developing eczema include:
- Family history: Children with a family history of eczema are more likely to develop the condition.
- Allergies: Eczema is often associated with allergies to certain foods, such as milk, eggs, and peanuts.
- Environmental triggers: Certain environmental factors, such as dust mites, pet dander, and harsh soaps, can trigger eczema flare-ups.
- Immune system dysfunction: Eczema is thought to be related to an overactive immune system that reacts to harmless substances as if they were harmful.
Symptoms of Baby Eczema
Eczema can affect any part of the body, but it is most commonly found on the face, neck, elbows, and knees. The symptoms of eczema can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Dry, itchy skin: The skin may feel rough and scaly and may itch intensely.
- Redness and inflammation: The affected skin may appear red and inflamed.
- Blisters and oozing: In severe cases, eczema can cause blisters and oozing.
- Cracking and bleeding: The skin may become cracked and bleeding, especially if it is scratched.
- Sleep disturbances: The itching and discomfort of eczema can make it difficult for children to sleep.
Diagnosis of Baby Eczema
Eczema is typically diagnosed based on a physical examination of the skin. Your doctor may also ask about your child’s medical history and family history of eczema. In some cases, your doctor may order blood tests or skin biopsies to rule out other conditions.
Treatment of Baby Eczema
There is no cure for eczema, but there are effective treatments that can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected children. Treatment options may include:
- Moisturizers: Regular use of a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce itching.
- Emollients: Emollients are similar to moisturizers, but they contain more oil and are better at sealing in moisture.
- Topical corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroids are medications that are applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: Calcineurin inhibitors are medications that are applied directly to the skin to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines can help reduce itching.
- Phototherapy: Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light to reduce inflammation.
- Wet wraps: Wet wraps involve wrapping the affected skin in wet bandages to help hydrate the skin and reduce itching.
Managing Baby Eczema
In addition to medical treatment, there are a number of things you can do to help manage your child’s eczema at home:
- Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid any triggers that seem to make your child’s eczema worse.
- Keep the skin clean: Bathe your child regularly with lukewarm water and a mild, fragrance-free soap.
- Moisturize regularly: Apply a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer to your child’s skin several times a day.
- Use emollients: Emollients can help seal in moisture and protect the skin from irritants.
- Avoid scratching: Scratching can worsen eczema and lead to infection. Keep your child’s nails trimmed short and cover their hands with mittens or socks at night to prevent them from scratching.
- Dress your child in soft, loose-fitting clothing: Avoid clothing made from rough or irritating materials, such as wool or synthetic fibers.
- Use a humidifier: A humidifier can help add moisture to the air and reduce dry skin.
- Manage stress: Stress can trigger eczema flare-ups. Help your child manage stress through activities such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.
Complications of Baby Eczema
Eczema can lead to a number of complications, including:
- Skin infections: Eczema can make the skin more susceptible to infections, such as staph infections.
- Sleep disturbances: The itching and discomfort of eczema can make it difficult for children to sleep.
- Emotional problems: Eczema can cause children to feel self-conscious and embarrassed about their appearance.
- Increased risk of asthma and allergies: Children with eczema are more likely to develop asthma and allergies.
Prognosis for Baby Eczema
Eczema is a chronic condition that can last for months or even years. However, with proper treatment and management, most children with eczema can live full and active lives.
When to See a Doctor
If your child has eczema, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment plan. You should also see a doctor if your child’s eczema is severe, if it is not responding to treatment, or if you have any concerns about your child’s health.
Additional Resources
