Baby Thrush: A Comprehensive Guide for Parents
Introduction
Baby thrush, also known as oral candidiasis, is a common infection caused by a type of yeast called Candida albicans. It affects the mouth and throat of infants and can cause discomfort, feeding difficulties, and other health problems if left untreated. This article provides a comprehensive guide for parents on baby thrush, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Causes of Baby Thrush
Candida albicans is a type of yeast that is normally present in small amounts in the mouths of infants. However, certain factors can lead to an overgrowth of Candida, resulting in baby thrush. These factors include:
- Antibiotic use: Antibiotics can kill off the good bacteria that normally keep Candida in check, allowing it to overgrow.
- Weak immune system: Infants with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to Candida infections.
- Diabetes: Infants with diabetes have higher levels of sugar in their saliva, which can provide a favorable environment for Candida growth.
- Premature birth: Premature infants have immature immune systems and are more likely to develop thrush.
- Maternal vaginal yeast infection: Candida can be passed from mother to baby during childbirth if the mother has a vaginal yeast infection.
Symptoms of Baby Thrush
The most common symptoms of baby thrush include:
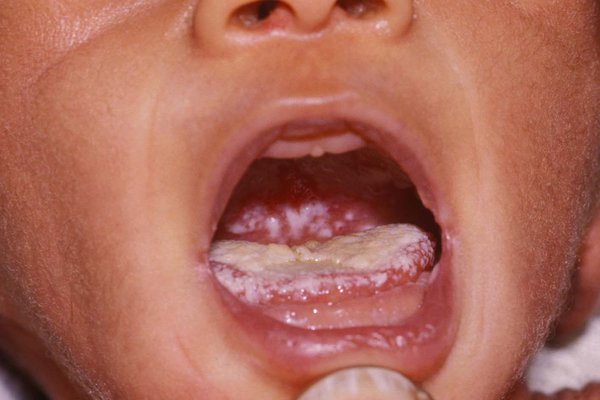
- White or yellow patches: Thick, white or yellow patches on the tongue, cheeks, gums, or roof of the mouth.
- Difficulty feeding: The patches can make it painful for infants to suck or swallow, leading to feeding difficulties.
- Irritability: Thrush can cause discomfort and irritability in infants.
- Diaper rash: Candida can also cause diaper rash, which appears as red, irritated skin in the diaper area.
Diagnosis of Baby Thrush
Baby thrush can be diagnosed by a healthcare provider through a physical examination of the infant’s mouth. The healthcare provider may also take a swab of the patches to confirm the presence of Candida.
Treatment of Baby Thrush
Treatment for baby thrush typically involves antifungal medications. These medications can be administered orally or topically.
- Oral medications: Oral antifungal medications, such as nystatin or fluconazole, are typically the first line of treatment for baby thrush. They are given to the infant by mouth and work by killing the Candida yeast.
- Topical medications: Topical antifungal medications, such as clotrimazole or miconazole, are applied directly to the affected areas in the mouth. They work by inhibiting the growth of Candida.
Treatment typically lasts for 7-14 days. It is important to complete the full course of treatment, even if the symptoms improve, to prevent the infection from recurring.
Prevention of Baby Thrush
There are several steps parents can take to help prevent baby thrush:
- Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly before handling your infant or touching their mouth.
- Clean pacifiers and bottles regularly: Sterilize pacifiers and bottles in boiling water or use a dishwasher with a sanitizing cycle.
- Avoid sharing utensils: Do not share spoons or other utensils with your infant.
- Treat maternal yeast infections: If you have a vaginal yeast infection, treat it promptly to prevent passing it on to your baby.
- Limit sugar intake: Avoid giving your infant sugary foods or drinks, as sugar can provide a favorable environment for Candida growth.
Complications of Baby Thrush
If left untreated, baby thrush can lead to several complications, including:
- Esophageal thrush: Candida can spread from the mouth to the esophagus, causing difficulty swallowing and pain.
- Systemic candidiasis: In rare cases, Candida can enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, causing a serious infection.
- Developmental delays: Untreated thrush can interfere with feeding and growth, leading to developmental delays.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention if your infant has any of the following symptoms:
- White or yellow patches in the mouth that do not go away after a few days
- Difficulty feeding or swallowing
- Irritability or fussiness
- Diaper rash that does not improve with treatment
Conclusion
Baby thrush is a common infection that can cause discomfort and health problems in infants. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of baby thrush, parents can help keep their infants healthy and happy. If you suspect your infant has baby thrush, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to ensure proper treatment and prevent complications.
