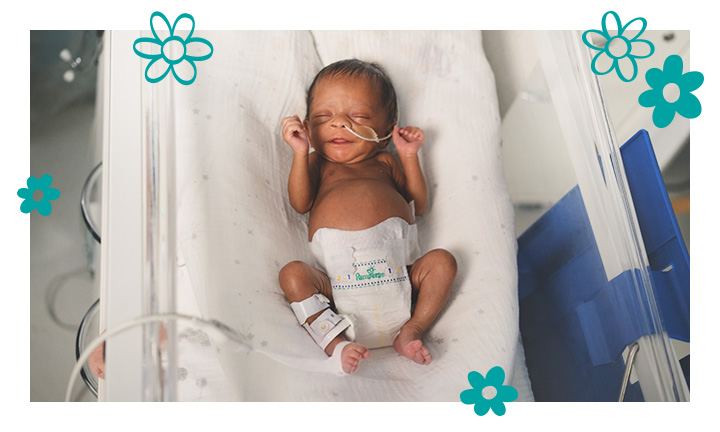
Premature Babies: Understanding the Challenges and Providing Optimal Care
Introduction
Premature birth, defined as the delivery of a baby before 37 weeks of gestation, is a significant global health concern. Premature babies face unique challenges and require specialized medical care to ensure their survival and long-term well-being. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of premature babies, including their characteristics, risk factors, potential complications, and the essential elements of their care.
Characteristics of Premature Babies
Premature babies are typically smaller and less developed than full-term infants. They may have underdeveloped organs, immature immune systems, and difficulty regulating their body temperature. Their skin is often thin and translucent, and they may have underdeveloped facial features.
Risk Factors for Premature Birth
Numerous factors can increase the risk of premature birth, including:
- Maternal age (under 17 or over 35)
- Multiple pregnancies
- Premature birth in previous pregnancies
- Certain medical conditions (e.g., preeclampsia, gestational diabetes)
- Substance abuse
- Poor nutrition
- Infections
Potential Complications of Premature Birth
Premature babies are at an increased risk of developing various complications, such as:
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS): A condition where the baby’s lungs are underdeveloped and unable to produce enough surfactant, a substance that helps the lungs expand.
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD): A chronic lung disease that can develop in premature babies who require prolonged mechanical ventilation.
- Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH): Bleeding in the brain, which can lead to neurological damage.
- Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC): A serious intestinal infection that can occur in premature babies.
- Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP): A condition that affects the development of the blood vessels in the retina, potentially leading to vision problems.
Essential Elements of Premature Baby Care
Providing optimal care for premature babies requires a multidisciplinary approach involving neonatologists, nurses, respiratory therapists, and other specialists. Key elements of their care include:
- Respiratory support: Premature babies often require respiratory support, such as mechanical ventilation or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), to help them breathe.
- Temperature regulation: Premature babies have difficulty regulating their body temperature, so they require a warm environment, such as an incubator or radiant warmer.
- Nutritional support: Premature babies may not be able to suck or swallow effectively, so they may need to be fed through a tube or intravenously.
- Infection prevention: Premature babies have immature immune systems, making them susceptible to infections. Strict infection control measures are essential.
- Monitoring and assessment: Premature babies require close monitoring of their vital signs, growth, and development to ensure their well-being.
Long-Term Outcomes of Premature Babies
The long-term outcomes of premature babies vary depending on the severity of their prematurity and any complications they experience. With advances in medical care, the survival rates of premature babies have improved significantly. However, they may face developmental delays, learning disabilities, and chronic health conditions.
Support for Families of Premature Babies
Families of premature babies often experience significant stress and anxiety. Support systems are crucial to help them cope with the challenges of caring for their premature infant. This support can include:
- Emotional support: Providing emotional support to parents and families through counseling, support groups, and peer connections.
- Educational resources: Educating families about premature birth, its potential complications, and the care their baby requires.
- Financial assistance: Helping families with the financial burden of medical expenses and lost income due to caring for their premature baby.
Conclusion
Premature babies are vulnerable infants who require specialized medical care and support to ensure their survival and long-term well-being. Understanding the challenges they face and providing optimal care is essential to improve their outcomes. By working together, healthcare professionals, families, and support systems can create a nurturing environment that promotes the growth and development of these precious little lives.